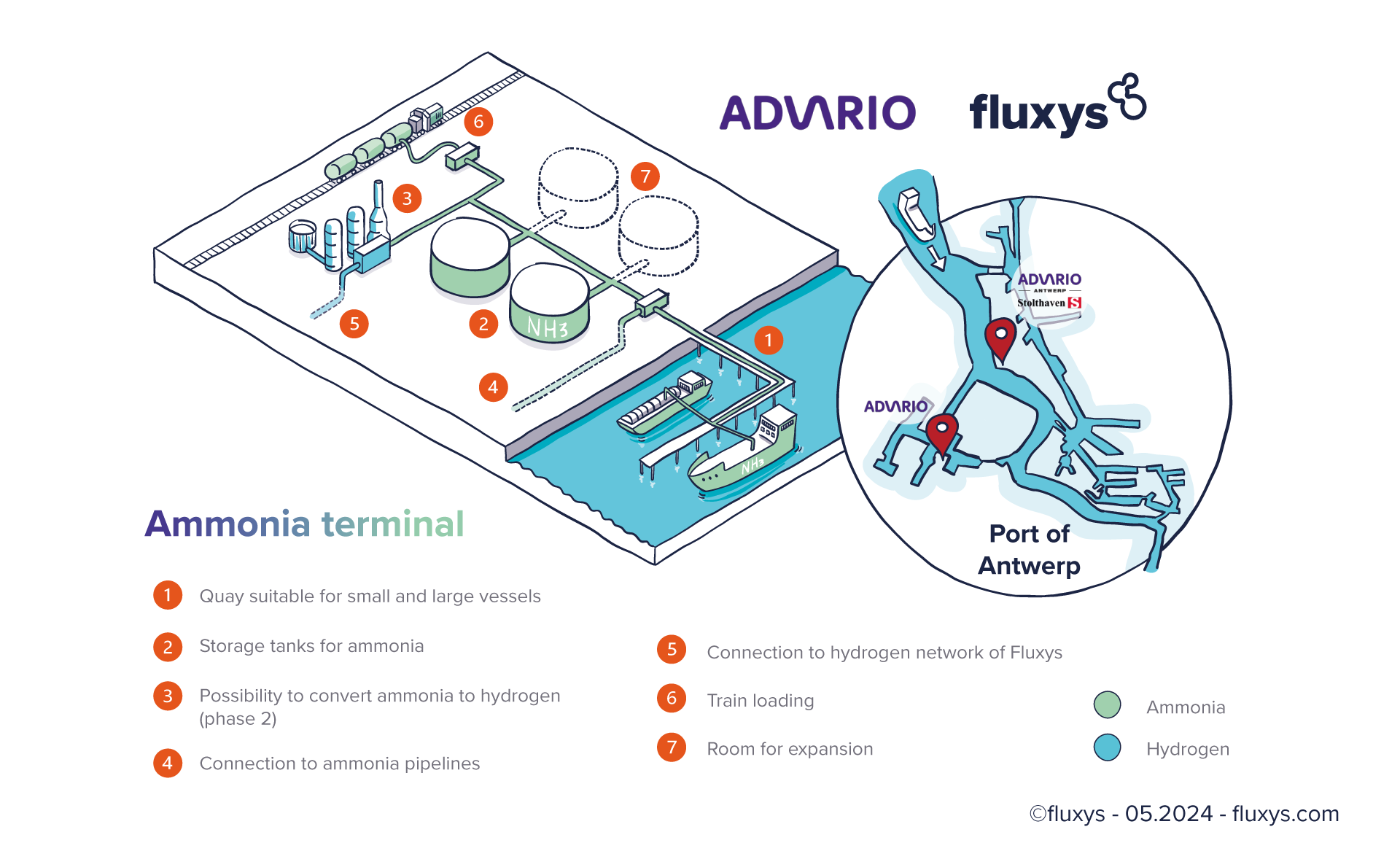
Fluxys and Advario have joined forces for the development of a state-of-the-art new ammonia (NH₃) terminal on the Advario Gas Terminal site in Antwerp.
This strategic partnership with Advario, a leading partner in ammonia and liquid storage logistics with a global network, aims to address the growing demand for the import of sustainable molecules in Europe and accelerate the region's transition towards decarbonisation.
- Third-party access
- Joint partnership (50-50%) between Fluxys and Advario; JDA signed
- Import terminal for renewable and low carbon ammonia as a carbon-neutral raw material and fuel
- Leveraging on the existing expertise, infrastructure and jetty of the Advario Gas Terminal
- Potential for conversion into hydrogen for transmission via the Fluxys hydrogen network.
- Status: feasibility study completed, moving to the FEED
Ammonia terminal and pipeline infrastructure
By combining their strengths and expertise in logistics, terminalling and pipeline transmission, Fluxys and Advario are developing an ammonia terminal and arranging the transport of ammonia via pipeline within the Port of Antwerp. Fluxys and Advario are now engaging with major industrial operators and suppliers to meet their evolving market demands.
The terminal, strategically located in the heart of the Antwerp port region, promises efficient connectivity and accessibility within Europe's largest petrochemical hub and its hinterland. Advario and Fluxys bring together their expertise in refrigerated storage and energy logistics ensuring the development of a robust and reliable infrastructure.
Interested in getting involved?
To involve stakeholders in the development process, Advario and Fluxys are launching the first step of their commercial process: an Expression of Interest.
The Expression of interest will gauge the interest and engage prospective partners with the aim of defining their needs, allocate capacities in the terminal and the associated ecosystem such as the NH₃ pipeline. Interested parties are invited to participate and contribute to shaping the future of NH₃ infrastructure in Europe.


European hub
The ammonia import terminal dovetails seamlessly with the partners’ strategy for implementing Europe's hydrogen strategy and the REPowerEU plan by providing decarbonisation infrastructure and effectively making Belgium a European hub for the import and export of molecules essential to the carbon-neutral economy. REPowerEU has set a target of 20 million tonnes of green hydrogen consumption by 2030, one fifth of which should be covered by ammonia imports.
Why import ammonia?
Ammonia is a key factor in the decarbonisation of Europe and importing it is an efficient way of bringing in large quantities of green energy and raw materials from overseas, where the abundance of solar and wind energy can be used to make hydrogen (H2), which can then be combined with nitrogen (N2) from the air to produce ammonia.
- Ammonia is a carbon-free molecule that is much more efficient and cheaper than hydrogen to store and transport in large volumes due to its higher energy density.
- At the destination port, the ammonia can be used as a raw material in the production of, for example, fertiliser, thus contributing to the global food supply and playing a key role in our everyday lives.
- It can also be used directly as a sustainable fuel in the shipping industry. Moreover, it can be converted back into green hydrogen, which in turn can power turbines, fuel cells and engines – all without any direct CO2 emissions. In other words, ammonia will help to cost-effectively decarbonise industrial processes. As a sustainable energy source, it can help Europe diversify its energy supply and reduce its carbon emissions.
Ammonia is a key molecule for industry that can be produced with low carbon footprint. The hydrogen-based fuel can be produced using renewable energy and contains no carbon components, so it does not cause any CO2 emissions. As such, industry can use ammonia (besides hydrogen) to decarbonise their processes and reduce carbon emissions.